Details of its wrath have consumed headlines for months at a time, and yet the complete magnitude of the California drought is perhaps not well understood by most. Certainly, the seeming abundance of drinking water in the cities of California belies the true nature of an issue that continues to get worse. Perhaps one of the greatest ironic conundrums that land organisms on earth must encounter is reconciling the relative scarcity of drinking water ![]() with an indisputable truth that most of the planet is covered in water. Unfortunately, sea water has very high salinity which makes it undrinkable and unsuitable for agriculture.
with an indisputable truth that most of the planet is covered in water. Unfortunately, sea water has very high salinity which makes it undrinkable and unsuitable for agriculture.
 iCalifornia as a state harbors some of the most fertile lands in Western United States, producing $18.18 billion in export value according to 2012 statistics.1 Production of food crop involves more than 400 different commodities ranging from almonds to zucchini, with California taking first place in profits and revenues associated with agriculture at a whopping $44.7 billion.2 As one of the most important agricultural States, the maintenance of high crop yields not only relies upon a blessing of highly fertile lands but also a continuous supply of water. The availability of water forms the basis of any agricultural establishment. Thus, the legends of the native Indian rainmaker 3 ring hard and true for Californian farmers nurturing fields that have barely received their fair share of seasonal rains, waiting for the rain maker to bring back peace and prosperity to their fields. The lack of agricultural productivity not only represents a significant economic burden, but a potential catastrophe for the cities and towns being sustained on Californian food crop.
iCalifornia as a state harbors some of the most fertile lands in Western United States, producing $18.18 billion in export value according to 2012 statistics.1 Production of food crop involves more than 400 different commodities ranging from almonds to zucchini, with California taking first place in profits and revenues associated with agriculture at a whopping $44.7 billion.2 As one of the most important agricultural States, the maintenance of high crop yields not only relies upon a blessing of highly fertile lands but also a continuous supply of water. The availability of water forms the basis of any agricultural establishment. Thus, the legends of the native Indian rainmaker 3 ring hard and true for Californian farmers nurturing fields that have barely received their fair share of seasonal rains, waiting for the rain maker to bring back peace and prosperity to their fields. The lack of agricultural productivity not only represents a significant economic burden, but a potential catastrophe for the cities and towns being sustained on Californian food crop.
Drought Overview
A drought can be generally described as a prolonged absence of adequate water supplies,4 which tends to be characterized by long periods without rain. Approximately 55-58% of the land mass in California is facing drought conditions,5 with Governor Jerry Brown declaring a state of emergency in January 2014 to combat quickly depleting water resources.6 To fully grasp the context of the California drought, it is best to briefly discuss the current water infrastructure and geography of California.
groundwater
![]() aquifers refilled by seasonal rains and tributaries stemming from the major California rivers. The issue is further compounded by the resistance of local agencies to redistribute water resources in the North to the agriculturally productive regions of the South-Central.8 Therefore, apart from a few water redistribution projects, namely the California aqueduct as a prime example,9 several agricultural regions in the productive central valley are facing extreme water shortages stemming from the lack of rains meant to irrigate fields.
aquifers refilled by seasonal rains and tributaries stemming from the major California rivers. The issue is further compounded by the resistance of local agencies to redistribute water resources in the North to the agriculturally productive regions of the South-Central.8 Therefore, apart from a few water redistribution projects, namely the California aqueduct as a prime example,9 several agricultural regions in the productive central valley are facing extreme water shortages stemming from the lack of rains meant to irrigate fields.
Reasons for Drought

The manifestation of drought conditions still remains a mystery that is multifaceted in nature. As a condition emerging from the lack of precipitation and marked ocean temperatures ![]() , which influence precipitation on land, have also been implicated in causing drought. While a drought may be a mechanistic mystery, human influences on creating climate change cannot be ignored as one of the principle causes of drought.
, which influence precipitation on land, have also been implicated in causing drought. While a drought may be a mechanistic mystery, human influences on creating climate change cannot be ignored as one of the principle causes of drought.
Drought Impact
The drought is undoubtedly impacting our lives in the form of far reaching consequences that extend beyond agricultural losses. Let’s take a closer look at some of these drought consequences:
- Agriculture and Economy: As discussed earlier, the financial impact of the drought is already being hard felt with 3% revenue losses attributed to water shortages. This amounts to a whopping $1-2 billion loss, as well as the loss of 17,000 jobs in the agricultural sector.11 Thankfully, at the moment there are no signs of large scale price increases for food items in the stores, but such a luxury could be quickly lost if present conditions continue. Already, several farms have been switching to much less water intensive crop or more profitable crop on a pound per pound basis such as the switch from cotton to almonds.12 The high cost of water has also pushed many farms to adopt expensive drip irrigation systems that may translate into higher food prices for the consumer in the future. Less fortunate farms must leave acres and acres of land unplanted.
https://web.archive.org/web/20160404102016if_/http://www.youtube.com/embed/wHSfugqQo8o iii - Drinking Water: Due to the limited supply of surface water, drought conditions may push for the use of drinking water to rural communities. The continual over usage of groundwater for agriculture without aquifer renewal may endanger thousands living in rural communities who depend on groundwater for basic sustenance.
- Reduction of Clean Energy: A collection of 1400 dams interspersed within the state help provide fossil fuel utilization and emissions.
- Ecosystem Destruction: The loss of biodiversity . In addition, drought conditions dramatically increase the risk of forest fires that may damage homes and destroy large swathes of productive forest land. It is no wonder that governor brown has implemented a larger recruitment of firefighters are part of his emergency declaration for the current California drought.
What You Can Do
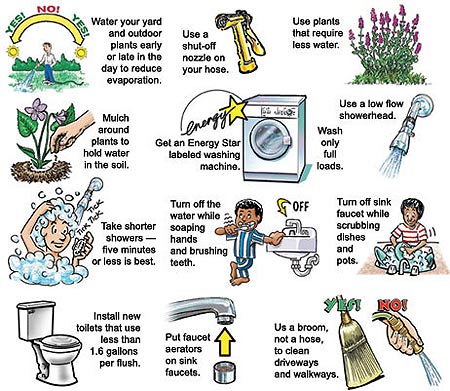
The drought cannot merely be quantified as an economic and agricultural issue. Behind it lie the faces of thousands that continue to feel the drought’s devastating effects. Fortunately, our actions can collectively make a significant impact. Currently, a whopping 23,275 gallons of water is utilized in California’s residential sector on a monthly basis. California’s official goal is to reduce this number by 20% in the next 6 years.18 Given the large burden that residential water usage places on the overall supply, there is an endless list of water saving techniques that could drastically reduce water consumption.19 This list is predicated on a broader culture of conservation that needs to be practiced in the household. Let’s take a look at some techniques we should be focusing on to save water:
- Check for Leaks: Over time, leaks in sinks, toilets can drastically deplete water if left unchecked. Using your water meter to detect losses can enable you to check your leaks and find them before any major losses pinch both your wallet and the environment. It might be helpful to have a plumber conduct an inspection of your home on an annual basis, and ensure proper utilization of water for residential purposes.
- Be a Responsible Consumer: Perhaps one of the most significant factors in drought management is managing the way individuals consume by promoting greater outreach and education of the issue at hand. Common sense is a great ally in our effort to reduce water consumption. Basic measures such as minimizing running water during dish washing and tooth brushing can go a long way in preventing excessive water waste. In fact, using a dishwasher is far more efficient when running at full loads than hand washing dishes.20 Similarly, laundry washing machines should be run only at full loads with high efficiency detergents optimized for high efficiency machines that minimize water utilization.21 Taking long showers is an absolute cardinal sin for water efficiency, and insulting pipes can prevent excessive water runs while waiting to heat up shower water. Nowadays, one can buy water saving shower heads and low flow faucets 22 that minimize shower water use to 2.5 gallons per minute instead of a whopping 10 gallons per minute. There are even more ways to save water, including replacing your toilet float with a water bottle to minimize the amount of toilet water in the bowl during each flush, to limiting your total flushes, all of which I leave at your discretion to follow.
- Smart Gardening: Finally, the most ideal mechanism to save water on gardening would be to replace your garden with artificial turf 23 that requires absolutely no water. If such a compromise is not possible, there are numerous means to minimize water usage in the garden. Starting from the top down, one should plant drought resistant plants in their gardens such as desert mallow and buckwheats.24 Applying a layer of mulch around plants will slow evaporative loss of water from soil and improve water retention of the soil. Repositioning sprinklers to exclusively hit planted areas can work wonders in the long run, along with a watering practice of deep soaking your lawn to allow for moisture to reach as far down in the root level as possible during watering. Watering early in the mornings, devoid of high winds, is also ideal to prevent pest growth and minimize evaporative loss.25
 iv
iv
Conclusion
The California drought represents a major environmental and humanitarian issue that must be addressed in an appropriate manner. Politically, there should be a greater push for pollution control regulation and water access projects that allow for greater redistribution of water resources. In terms of outreach, a much greater effort is needed towards promoting education on the current nature of the drought and methods to mitigate its harmful effects through water conservation. Most importantly, however, is our collective responsibility as global citizens to implement our knowledge in securing our hydrological future.





